RPFT Online Practice Questions and Answers
A 9-year-old girl had an FVC of 2.35 L1 year ago. She was 122 cm (4 ft) tall and weighed 29.5 kg (65 lb). Her current height is 127 cm (4 ft 2 in), and her weight is 34 kg (75 lb). The current FVC measurement is
2.20 L. The quality of both tests met ATS/ERS goals. A pulmonary function technologist should conclude the change is
A. Not significant since it is less than a 15% decrease.
B. Not significant since it is within normal test variability.
C. Significant since a decline is not expected.
D. Significant since her weight has changed.
During a cardiopulmonary stress test using breath-by-breath gas analysis, a pulmonary function technologist notices that the VO2 suddenly decreases. Which of the following may explain this change?
1.
The patient has achieved anaerobic threshold.
2.
The measurement of the expired gas volumes is inaccurate.
3.
O2 analyzer "phase delay" has increased.
4.
There is a leak in the tubing or mouthpiece.
A. 1, 3, and 4 only
B. 1, 2, and 3 only
C. 1, 2, and 4 only
D. 2, 3, and 4 only
During a linearity check of a flow sensor in a plethysmograph with a 3-liter calibration syringe, a pulmonary function technologist observes the following:
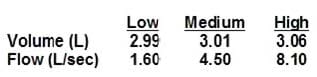
Which of the following should the technologist do?
A. Perform an additional flow check at 10 L/sec.
B. Look for an obstruction in the flow sensor.
C. Record these results and begin testing.
D. Recalibrate and repeat the linearity check.
A pulmonary function technologist is performing an exercise study on a patient with sarcoidosis. Which of the following end-tidal CO2 values should the technologist expect at rest, if the test is performed appropriately?
A. 7-10%
B. 0-1.5%
C. 4-5%
D. 2-3%
During a bronchial provocation study, a patient has the following spirometric values after a 0.25 mg/mL dose of methacholine:
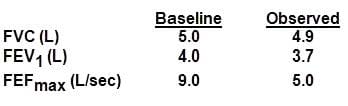
Based on these results, a pulmonary function technologist should
A. Instruct the patient to blow out longer and repeat the effort.
B. Stop the test and immediately administer a bronchodilaior.
C. Instruct the patient to blow out harder and repeat the effort.
D. Reduce the concentration of methacholine on the next trial.
While performing a quality control test on an open circuit nitrogen system, the volume of a 3-liter syringe is measured as 3.9 L. Which of the following is the most probable explanation?
A. There was an air leak in the system.
B. The initial O2 concentration in the syringe was greater than 0.21.
C. The volume was not corrected from ATPS to BTPS.
D. The nitrogen analyzer gain was set too low.
A polarographic oxygen analyzer used to measure expired gas in a metabolic system should always be calibrated with
A. Gas concentrations higher and lower than the expected measurement
B. Oxygen mixtures containing 4% and 8% carbon dioxide
C. 100% oxygen and 100% nitrogen, fully saturated
D. Air and fully saturated 100% oxygen.
A pulmonary function technologist is asked to select gas concentrations to simulate pediatric patients' exhaled concentrations during a DLco simulation. Which of the following FECO concentrations should the technologist select?
A. 0.200
B. 0.300
C. 0.400
D. 0.100
Prior to performing a multiple-breath U2 washout test, a pulmonary function technologist is unable to zero the H2 gas analyzer. Which of the following may be responsible?
A. Inadequate vacuum
B. Exhausted fuel cell
C. Chopper motor failure
D. Condensation of water
Prior to an exercise study, a pulmonary function technologist finds that the patient's RER is 1.13. Which of the following best explains this finding?
A. Carbohydrate metabolism
B. Protein metabolism
C. Hypoventilation
D. Hyperventilation
A pulmonary function technologist reviews the following home monitoring spirometry results:
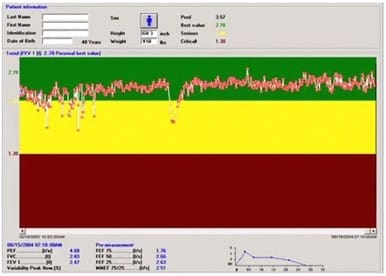
According to National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP) guidelines, what feedback should the technologist give to the patient regarding test performance?
A. Ask the patient to blow out longer.
B. Encourage the patient to continue testing and monitoring the FEW
C. Ask the patient to recalibrate the spirometer.
D. Come into the office for further instructions on proper testing technique.
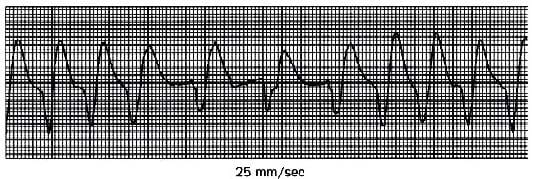
The ECG above is recorded during the recovery phase immediately following termination of an ergo meter exercise study. A pulmonary function technologist should
A. Initiate chest compressions
B. Have the patient lie down
C. Check the electrode connections
D. Continue the cool-down phase
A pulmonary function technologist is performing quality control on a nebulizer used in the 5-breath dosimeter bronchial challenge. The target output of the device is 0.09 mL, plus or minus 10%. After 10 actuations, the nebulizer output was 75 礚 with a 2.0 mL initial saline dose in the nebulizer. The technologist should
A. Open the vent before starting the bronchial challenge.
B. Add an exhalation filter and proceed with testing patients.
C. Clean and reevaluate this nebulizer.
D. Accept the results and begin using the device.
Which of the following is the most reliable indicator that a patient has achieved his maximum exercise capacity during a progressive exercise (stress) test?
A. Respiratory exchange ratio greater than 0.8
B. Heart rate of 210/min
C. VO2 remains stable with increasing workload
D. Minute ventilation greater than 170 L/min
The following results are obtained from an adult male: The corrected DLco value

A. is unchanged.
B. is higher.
C. is lower.
D. cannot be calculated.
