HPE6-A48 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Refer to the exhibit.

A 7008 Branch Office Controller (BOC) is deployed in a remote office behind a core router. This core router does not support 802.1q encapsulation. The Mobility Controller (MC) is the gateway for two tunneling mode SSIDs, as shown in the exhibit.
Which two different configuration options ensure that wireless users are able to reach the branch network through the router? (Select two.)
A. Configure all ports of the BOC as access ports on the controller VLAN, and change the gateway of clients to the core router IP.
B. Configure the uplink of the BOC as an access port on the controller VLAN, and enable NAT for the SSID VLANs.
C. Configure the uplink of the BOC as a trunk port, tagging the controller and the SSID VLANs, and enable NAT for the SSID VLANs.
D. Configure the uplink of the BOC as an access port on the controller VLAN, and add static router in the router for the SSID VLAN subnets.
E. Configure the uplink of the BOC as a trunk port that permits the controller and the SSID VLANs. The controller VLAN must be native.
A customer with a multi-controller network upgrades the ArubaOS from 6.4 to 8. The customer's clients must be able to move between different locations of the campus without disconnecting their applications, when roaming or if there are Mobility Controller (MC) failures. The customer also wants to have full control of the users, and be able to change their session properties from a RADIUS server.
Which steps must the network consultant include in the implementation plan to meet these requirements?
A. 1. Create a controller cluster profile that contains the management and VRRP IP addresses of each member.
2.
Apply the profile to all MCs in the cluster.
3.
Confirm that the cluster is L2 connected.
B. 1. Configure a VRRP instance for all MCs
2.
Create a controller cluster profile that contains the management IP and VIP addresses of each MC.
3.
Apply the profile to all MCs in the cluster.
4.
Confirm that the cluster is L2 connected.
C. 1. Configure a VRRP instance for each MC.
2.
Create a controller cluster profile that contains the management IP of each member.
3.
Apply the profile to all MCs in the cluster.
4.
Confirm that the cluster is L3 connected.
D. 1. Create a controller cluster profile that contains the management and VRRP IP addresses of each member.
2.
Apply the profile to the cluster leader.
3.
Confirm that the cluster is L2 connected.
Refer to the exhibits. Exhibit 1
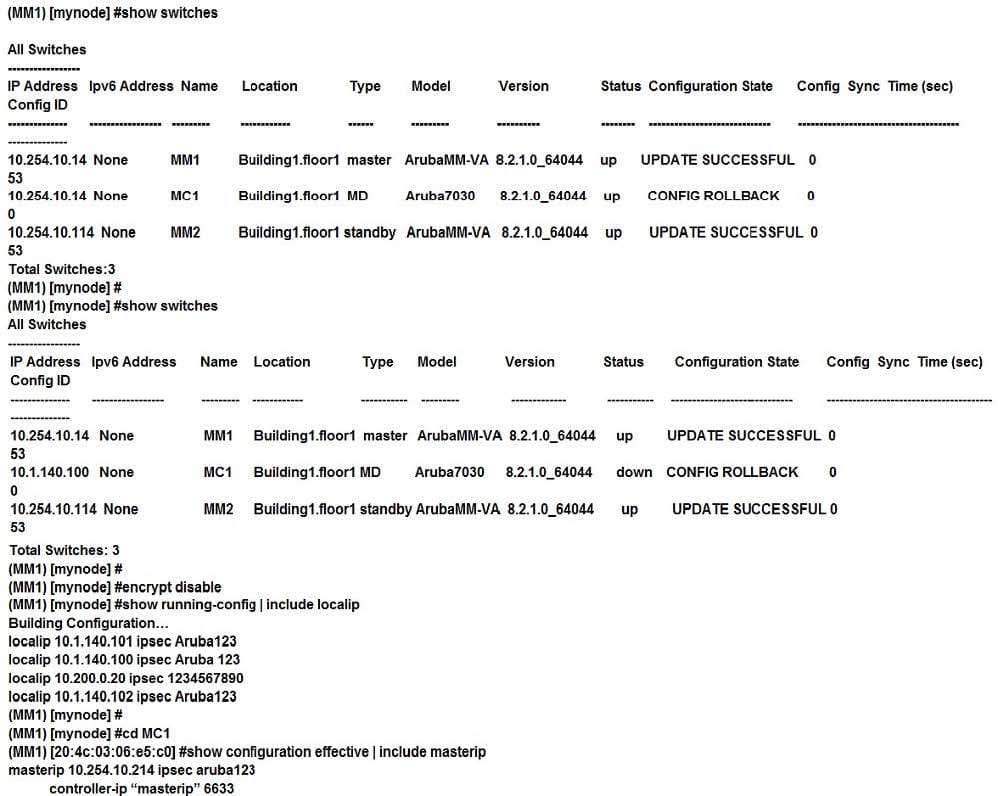
Exhibit 2 Exhibit 3

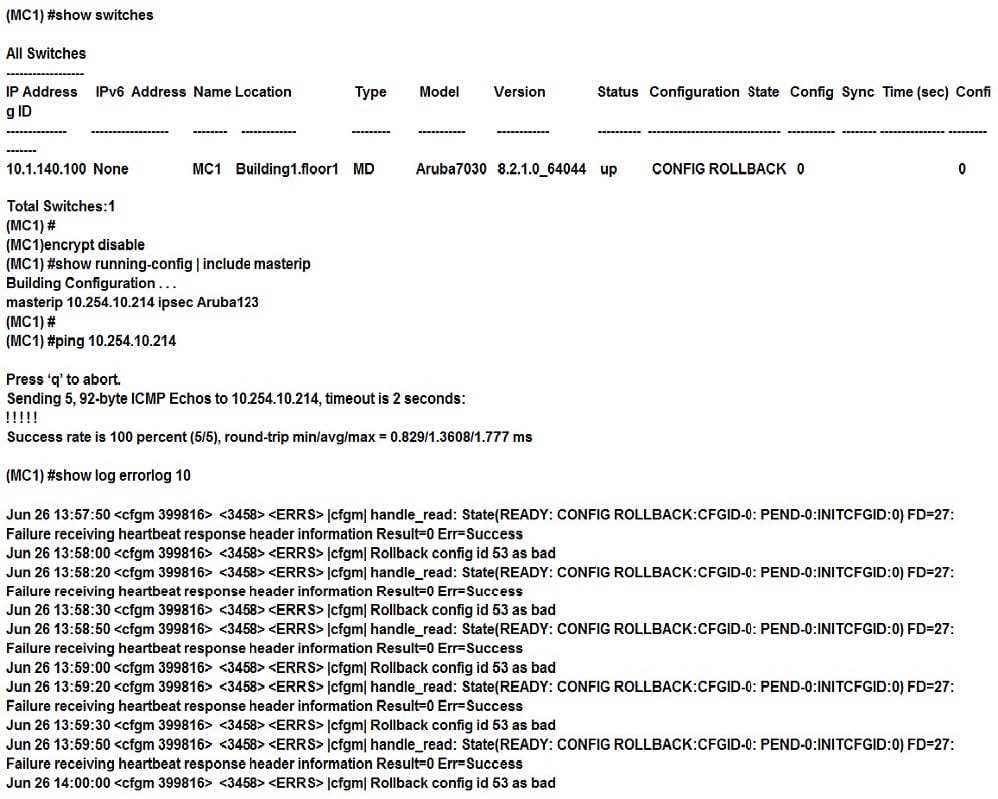
A network administrator deploys a Mobility Master (MM) pair with the VRRP VIP equal to 10.254.10.214, and attempts to associate MC1 to it. At first, the integration appears to be successful. However after a few minutes the network administrator issues the show switches command and sees that the MC1 is down, even though the device is up and running.
Every time the network administrator reboots the Mobility Controller (MC), the MC shows as being up and then it shows as being down. The network administrator gathers the information shown in the exhibits.
What should the network administrator do to resolve this problem?
A. Change the localip ipsec key to Aruba123 in the mynode device level from the MM, save, and reboot.
B. Enable disaster recovery mode in MC1 and change the masterip ipsec key to Aruba 123, save, and reboot.
C. Change the masterip ipsec key to Aruba123 in the device level from the MM, save, then reboot MC1.
D. Wipe out the configuration in MC1 and reboot, then run the full-setup configuration dialog all over again.
Several users are connected to the same WLAN and want to play the same multicast-based video stream. The network administrator wants to reduce bandwidth consumption and at the same time increase the transmit rate to a fixed value for WMM marked video streams in a large-scale network. Broadcast Multicast Optimization (BCMCO) is already on.
Which two configuration steps does the network administrator have to perform to optimize the multicast transmissions? (Select two.)
A. Enable Dynamic Multicast Optimization (DMO) and set forwarding mode to tunnel in the VAP profile.
B. Enable Broadcast Multicast Rate Optimization (BC/MC RO) in the SSID profile.
C. Enable Broadcast Multicast Optimization (BCMCO) and set forwarding mode in the VAP.
D. Disable Broadcast Multicast Optimization (BCMCO) in the VLAN.
E. Set Video Multicast Rate Optimization (VMRO) in the SSID profile.
Refer to the exhibit.

A network administrator wants to allow contractors to access the WLAN named EmployeesNet. In order to restrict network access, the network administrator wants to assign this category of users to the contractor firewall role.
To do this, the network administrator configures ClearPass in a way that it returns the Aruba-User-Role VSA with the contractor value. When testing the solution the network administrator receives the wrong role.
What should the network administrator do to assign the contractor role to contractor users without affecting any other role assignment?
A. Set contractor as the default role in the AAA profile.
B. Create the contractor firewall role in the MC.
C. Create server derivation rules in the server group.
D. Check the Download role from the CPPM option in the AAA profile.
A software development company has 700 employees who work from home. The company also has small offices located in different cities throughout the world. During working hours, they use RAPs to connect to a datacenter to upload software code as well as interact with databases.
In the past two months, brief failures have occurred in the 7240XM Mobility Controller (MC) that runs ArubaOS 8.3 and terminates the RAPs. These RAPs disconnect, affecting the users connected to the RAPs. This also causes problems with code uploads and database synchronizations. Therefore, the company decides to add a second 7240XM controller for redundancy.
How should the network administrator deploy both controllers in order to provide redundancy while preventing failover events from disconnecting users?
A. Connect both controllers with common VLANs, and create an L2-connected cluster using public addresses in the internet VLAN.
B. Connect both controllers with common VLANs, and create an HA fast failover group with public addresses in the internet VLAN.
C. Connect both controllers with different VLANs, and create an L2-connected cluster using private addresses in the internet VLAN.
D. Connect both controllers with common VLANs, and configure LMS/BLMS values equal to public addresses in the internet VLAN.
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
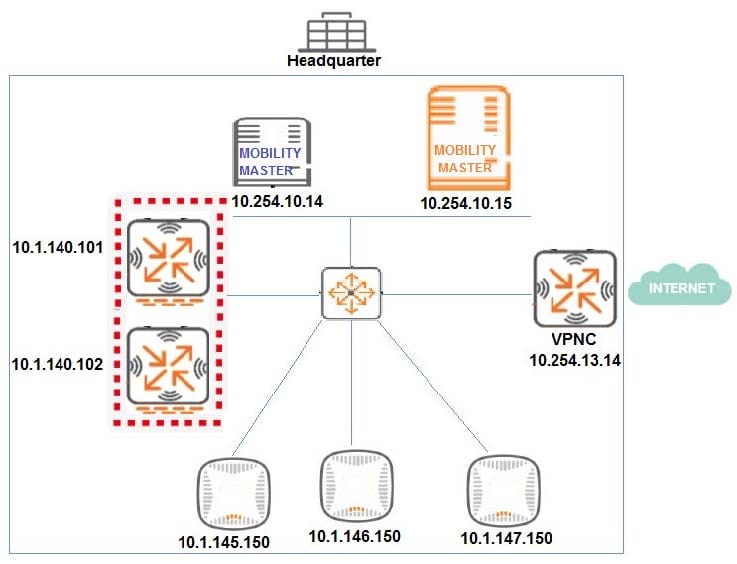
Exhibit 2

Exhibit 3

A network engineer deploys a Master Controller (MC) cluster at Headquarter to offer high levels of redundancy, and prepares the wired side of the network. This preparation includes the VLAN, DHCP Settings, and unicast routing services that APs require to reach the cluster.
The network engineer waits for 20 minutes after connecting the APs and sees that no SSIDs are advertised. The network engineer logs into one of the MCs and one of the AP's consoles to obtain the outputs shown in the exhibits.
What can the network engineer do to fix the APs discovery process, to ensure the best scalability even if one MC fails?
A. Reprovision the APs with a different Master IP.
B. Modify the IP address in one of the MCs.
C. Modify option 43 in the DHCP pool.
D. Create a VRRP instance in the MCs.
Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator deploys a Mobility Master (MM)-Mobility Controller (MC) network with APs in different locations. Users in one of the locations report that the WiFi network works fine for several hours, ang then they are suddenly disconnected. The symptom may happen at any time, up to three times every day, and lasts no more than two minutes.
After some research, the network administrator logs into the MM and reviews the output shown in the exhibit.
Based on this information, the network administrator logs into the MM and reviews the output shown in the exhibit.
Based on this information, what is the most likely reason users get disconnected?
A. AirMatch is applying a scheduled optimization solution.
B. Users in the 2.4 GHz band are being affected by high interference.
C. Adpative Radio Management is reacting to RF events.
D. AirMatch is reacting to non-scheduled RF events.
Refer to exhibit.
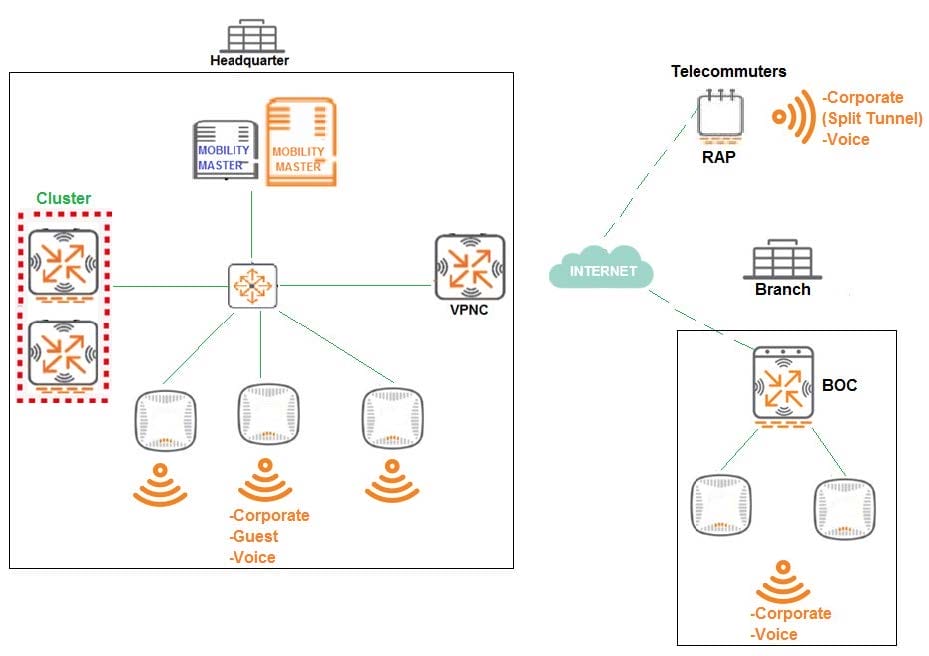
A company has a multiple Arua implementation with three different locations named Headquarter, Branch,
and Telecommuters.
The network design includes the following:
Headquarter APs terminate at the Mobility Controller (MC) cluster and propagate Corporate, Guest, and
Voice SSIDs
Branch APs terminate at the Branch Office Controller (BOC) and propagate Corporate and Voice SSIDs
BOC reaches the Mobility Master (MM) through a VPNC.
Telecommuter RAPs terminate at VPNC and propagate Corporate and Voice SSIDs.
The Corporate SSID on the RAPs is split-tunnel, all other SSIDs are tunnel.
The network design requires minimal AP group and VAP configuration effor, while preventing unnecessary
VAP propagation to lower hierarchy levels.
Following Aruba node hierarchy desing recommendations, which group hierarchy design helps meet these
requirements?
A. /md /md/Corp1/ /md/Corp1/Offices /md/Corp1/Offices/Headquarter /md/Corp1/Offices/Branch /md/Corp1/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
B. /md /md/Headquarter /md/Branch /md/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
C. /mm /md/Locations /md/Locations/Headquarter /md/Locations/Branch /md/Locations/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
D. /md /md/Location1/ /md/Location1/Branch /mdLocation1/Offices /md/Location1/Offices/Headquarter /md/Location1/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
Refer to the exhibit.
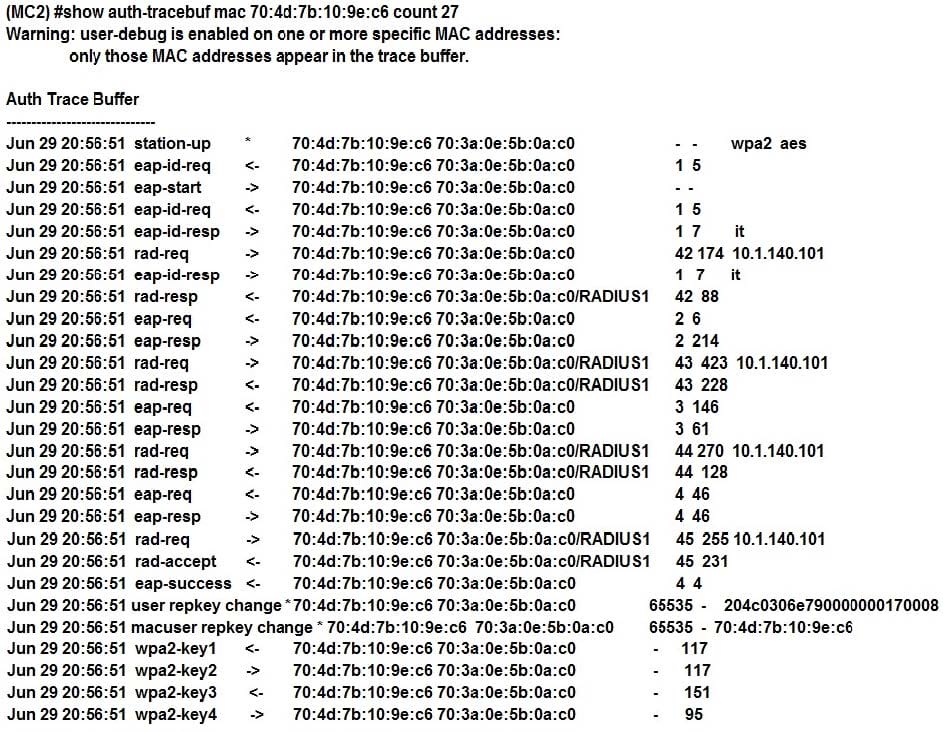
A network administrator is validating client connectivity and executes the show command shown in the exhibit. Which authentication method was used by the wireless station?
A. 802.1X user authentication
B. EAP authentication
C. 802.1X machine authentication
D. MAC authentication
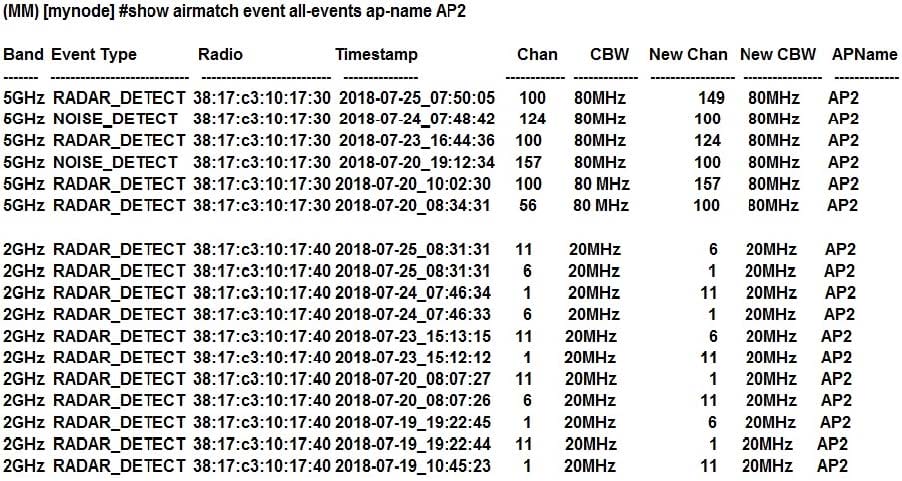
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
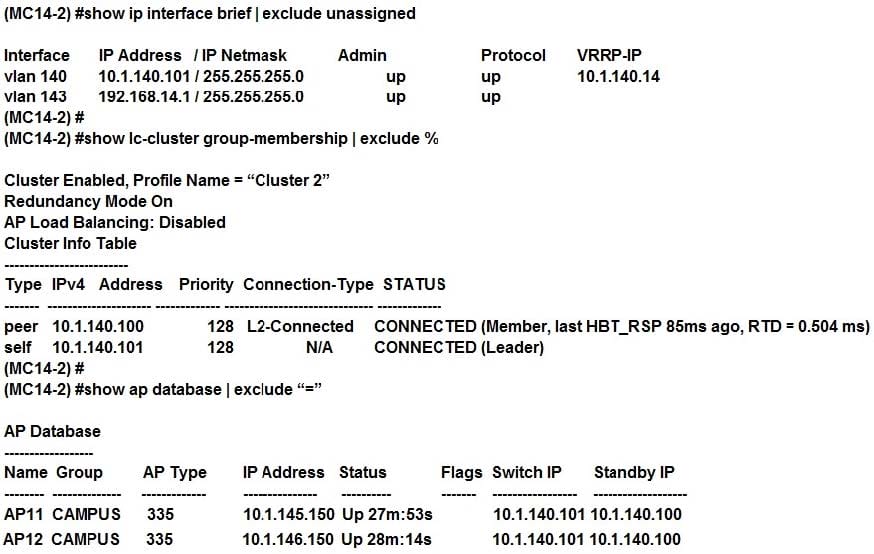
Exhibit 2
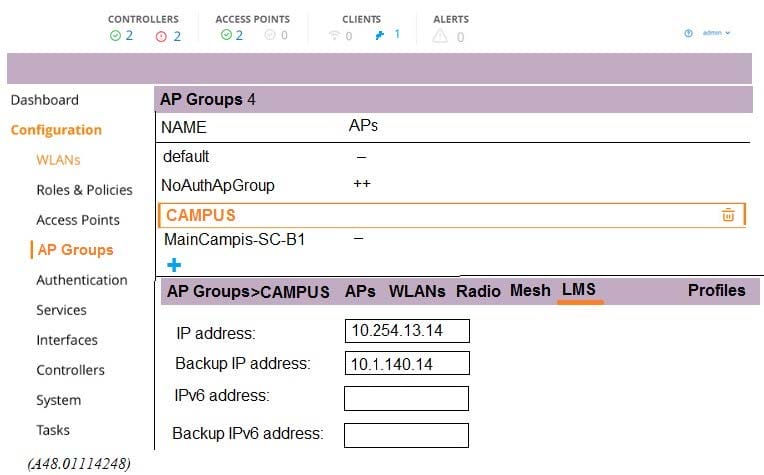
A network administrator deploys a test environment with two Mobility Masters (MMs), two two-member Mobility Controller (MC) clusters, and two CAPs, with the intention of testing several ArubaOS features, Cluster members run VRRP for AP boot redundancy. Based on the information shown in the exhibits, what is the current status of the APs?
A. APs are currently communicating with LMS IP, and 10.1.140.100 is S-AAC.
B. APs are currently communicating with BLMS IP, and 10.1.140.101 is A-AAC.
C. APs are currently communicating with BLMS IP, and 10.1.140.101 is S-AAC.
D. APs are currently communicating with BLMS IP, and 10.1.140.100 is A-AAC.
A financial institution contacts an Aruba partner to deploy an advanced and secure Mobility Master (MM)Mobility Controller (MC) WLAN solution in its main campus and 14 small offices/home offices (SOHOs). Key requirements are that users at all locations, including telecommuters with VIA, should be assigned roles with policies that filter undesired traffic. Also, advanced WIPs should be enforced at the campus only.
These are additional requirements for this deployment:
RAPs should ship directly to their final destinations without any pre-setup and should come up with the right configuration as soon as they get Internet access. Activate should be configured with devices MACs, serial numbers, and provisioning rules that redirect them to the standalone VMC at the DMZ Users should be able to reach DNS, FTP, Web and telephone servers in the campus as well as send and receive IP telephone calls to and from the voice 10.1.50.0/24 segment. Local Internet access should be granted.
Refer to the exhibit.
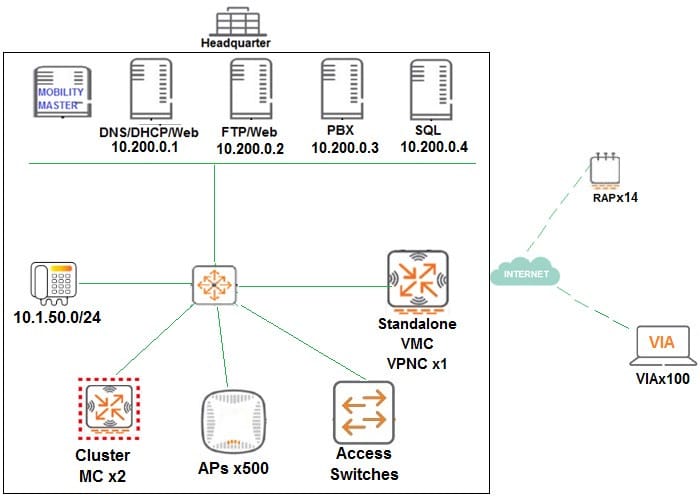
Refer to the scenario and the exhibit.
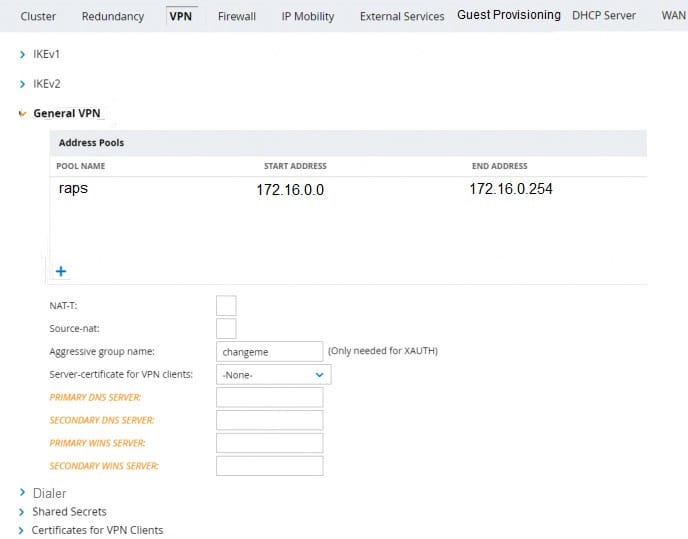
The standalone VMC will act as a VPN Concentrator of the RAPs. The network administrator configures the Standalone VMC with a pool of addresses and the SOHOs AP Group from the MM.
Which additional steps must the network administrator perform to allow the RAPs to terminate their IPSec tunnels and associate to the Standalone VMC?
A. Add RAP MAC addresses into the RAP whitelist, and associate them with the SOHOs AP-Group.
B. Add RAP MAC addresses into the CPSec whitelist, and associate them with the SOHOs AP-Group.
C. Configure the same IP Pool at the MM group level, then create user accounts for the RAPs in the internal database.
D. Create user accounts with the sys-ap-role, and define shared secrets to associate to RAP IP addresses at the MM group level.
Refer to the exhibit.
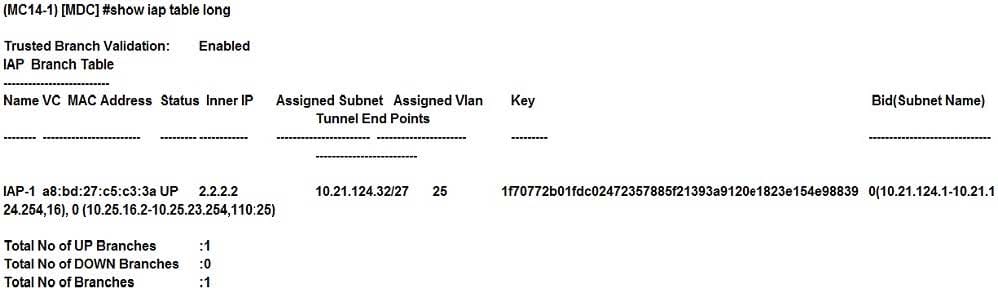
A network administrator configures an Instant AP (IAP) to establish an Aruba IPSec tunnel across the Internet, and configures two DHCP pools for wireless users.
Based on the output shown in the exhibit, which device behaves as a DHCP server for the users?
A. Mobility Master
B. Mobility Controller
C. External server
D. DSL modem
E. Virtual Controller
A network administrator needs to deploy L2 Mobility Master (MM) redundancy. MM1 uses IP address
10.201.0.10 and MAC address 1c:98:ec:25:48:50, and MM2 uses IP address 10.201.0.20 and MAC 1c:98:ec:99:8a:80. Both run VRRP process with VRID 201.
Which configuration should the network administrator use to accomplish this task?
A. /mm (MM1): database synchronize period 30 /mm/mynode (MM1): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.20 ipsec key123 /mm/mynode (MM2): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.10 ipsec key123
B. /mm (MM1): master-redundancy master-vrrp 10 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.20 ipsec key123 database synchronize period 30 /mm/mynode (MM2): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.10 ipsec key123
C. /mm/mynode (MM1): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.20 ipsec key123 database synchronize period 30 /mm/mynode (MM2): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.20 ipsec key123 database synchronize period 30
D. /mm (MM1): database synchronize period 30 /mm/mynode (MM1): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.10 ipsec key123 /mm/mynode (MM2): master-redundancy master-vrrp 201 peer-ip-address 10.201.0.20 ipsec key123
Refer to the exhibit.
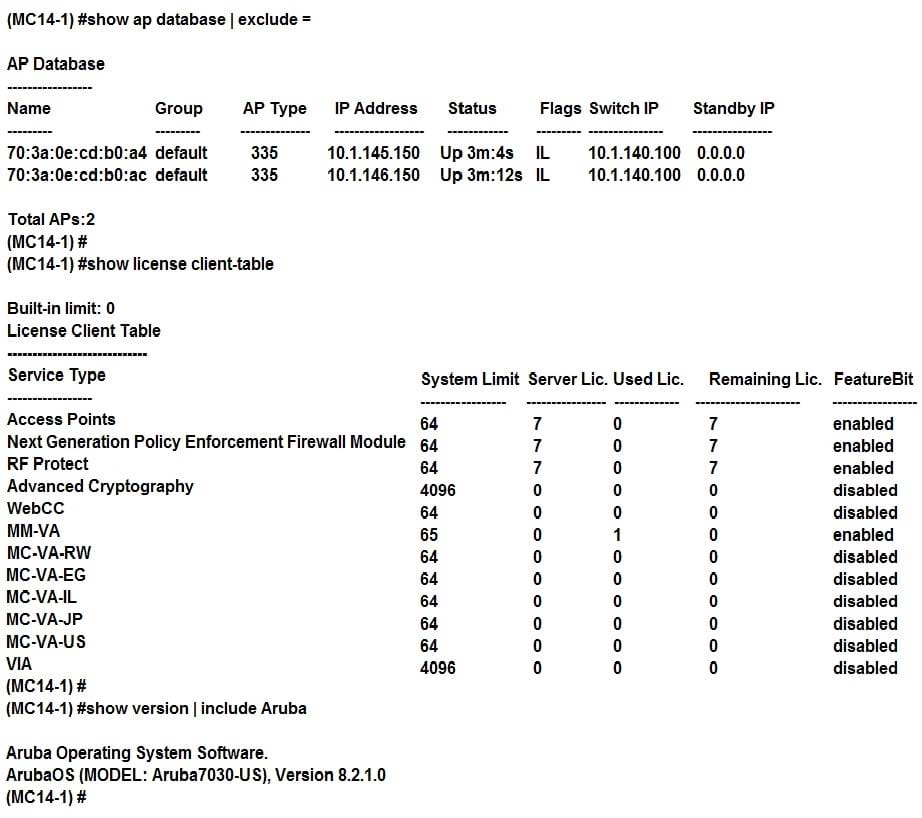
A network engineer configures some VAPs in customer groups and creates a pool of licenses with enough units for seven APs. The network engineer deploys the first two APs, looks at the ap database, and notices the APs are inactive and experience licensing-related issues.
Based on the show command outputs shown in the exhibit, what must the engineer do to solve the problem?
A. Allocate two more MM-VA licenses to the pool.
B. Allocate two more MC-VA-US licenses to the pool.
C. Allocate seven more MM-VA licenses to the pool.
D. Allocate seven more MC-VA-US licenses to the pool.
