HPE2-Z39 Online Practice Questions and Answers
A network administrator suspects that interfaces in a link aggregation have been accidentally connected to multiple switches. The administrator wants to find the hostnames of the switches on the other side of the interfaces. How can the administrator find this information?
A. Use the show lace command to view LACP information.
B. Use the show trunks command to view link aggregation information.
C. Use the show interface command to view detailed interface status.
D. Use the show lldp info remote-device command to view LLDP information.
What is a best practice for an MSTP region?
A. The config name should contain the hostname of the root switch.
B. The desired root for the CIST should have a lower config revision than any other switch.
C. Switch-to-switch links should carry all VLANs in use in the MSTP region.
D. A switch should have a consistent spanning tree priority in each MSTP instance
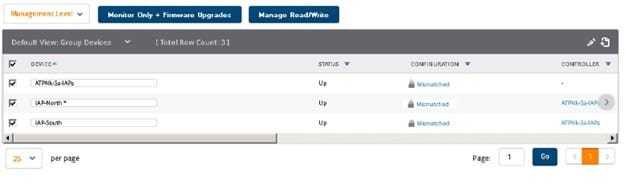
An Aruba Instant cluster is added in Aruba AirWave. A network administrator needs to change the cluster management level to Manage Read "Write. The exhibit shows the current status for the cluster.
What should the administrator do before changing the management level?
A. Check the cluster SNMP credentials and resolve the mismatch between the cluster credentials and AirWave credentials.
B. Verify that the cluster is configured with the same shared key that is configured in the global AirWave settings.
C. Investigate why the cluster configuration does not match the group configuration template and resolve any issues.
D. Determine why AirWave cannot contact the cluster and resolve any connectivity issues in the network.
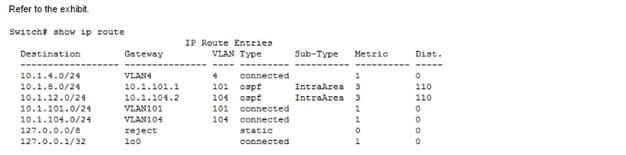
An ArubaOS switch has the routing table shown in the exhibit. A network administrator then enters this
command: Switch (config) # ip routs 10.0.0.0/8 10.1.104.2
After the administrator enters this command, packets arrive that are destined for 10.1.8.8 and 10.1.8.13.
What does the switch do with this traffic?
A. It load balances some of the traffic to 10.1.101.1 and some to 10.1.104.2.
B. It forwards at of the traffic to 10.1.104.2.
C. It drops the traffic.
D. It forwards all of the traffic to 10.1.101.1.
A network administrator manages an ArubaOS switch through the CLI The administrator needs to configure an untagged VLAN assignment on a range of interfaces. How should the administrator enter the untagged command to complete this configuration?
A. Create a manual, named interface range Then access the context for the range and specify the VLAN ID with the untagged command.
B. Access the context for a range of interfaces and specify the VLAN ID with the untagged command
C. Access the individual context for each of the interfaces and specify the VLAN ID with the untagged command
D. Access the VLAN context and specify a range of interfaces with the untagged command.
Two ArubaOS switches connect on a VLAN. and both enable OSPF on that VLAN. Which VLAN OSPF setting must match for the switches to become fully adjacent neighbors?
A. DR priority
B. area ID
C. cost
D. router ID
Network administrators need to access an ArubaOS switch CLI remotely. How can the administrator ensure that all data passed between management stations and the switch is encrypted?
A. Create local user accounts and enable command authorization.
B. Configure operator and manager passwords for Telnet access.
C. Create an SSH key. enable SSH. and disable Telnet.
D. Enable HTTPS access.
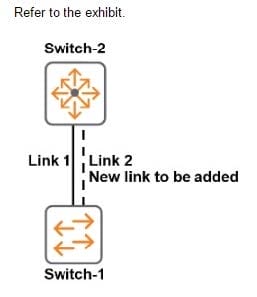
The switches in the exhibit use RSTP The network administrator needs to add Link 2. Why should the administrator configure Links 1 and 2 as a link aggregation?
A. to combine traffic statistics for the interfaces
B. to prevent a loop from occurring
C. to share traffic more evenly over both links
D. to automatically apply the settings already configured for Link 1 to Link 2
On an ArubaOS switch, what is the difference between an SNMPv2c community with manager unrestricted rights and an SNMPv2 community with operator unrestricted rights?
A. The manager unrestricted community has read-write access to all managed objects on the switch; the operator unrestricted community has read-write access to some objects but not to any Config objects.
B. The manager unrestricted community uses the Telnet/SSH password assigned to the manager to authenticate SNMP servers: the operator unrestricted community uses the Telnet/SSH password assigned to the operator.
C. The manager unrestricted community has read-write access to the switch, but the operator unrestricted community has read-only access.
D. The manager unrestricted community uses encryption, but the operator unrestricted community uses plaintext communication
What is the effect if a network administrator sets a spanning tree priority on an ArubaOS switch interface?
A. The interface priority helps to determine which switch on the link is elected root.
B. The interface priority determines whether this switch or the connected switch has the Designated port on the link.
C. The interface priority breaks a tie when multiple interfaces offer the same lowest cost path to the root through the same neighbor
D. The interface priority prevents a rogue switch connected to the interface from becoming root.
A company has a cluster of Aruba Instant APs (lAPs). The company wants to add a new IAP to the cluster. What should network administrators ensure before they connect the new IAP?
A. that the new IAP has been provisioned with an IP address and the IP address of the cluster virtual controller (VC)
B. that the switch port for the AP is untagged for the same VLAN as the current cluster
C. that Aruba Activate is configured with provisioning rules for the IAP
D. that the DHCP server has the correct options 60 and 43
A network administrator needs to configure Virtual Switching Framework (VSF) for the first time on an ArubaOS switch. The administrator enters this command:
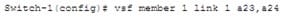
The administrator then wants to provision member 2 settings. What must the administrator do before provisioning these settings?
A. Specify the model type for member 1.
B. Configure SNMP settings that match settings configured on member 2
C. Join member 2 to the VSF fabric.
D. Enable VSF on the switch and reboot.

A broadcast packet arrives tagged for VLAN 2 on the Member 2 link of Trk2. What does Member 2 do?
A. It forwards the packet on its local link in Trk1.
B. It forwards the packet over the VSF link to Member 1, and then Member 1 forwards the packet on its link in Trk1.
C. It uses LACP to communicate with the commander on the VSF link, and then follows the commander directions.
D. It uses a hash to select one of the links in Trk1, and then forwards the packet locally or on the VSF link, based on the decision.
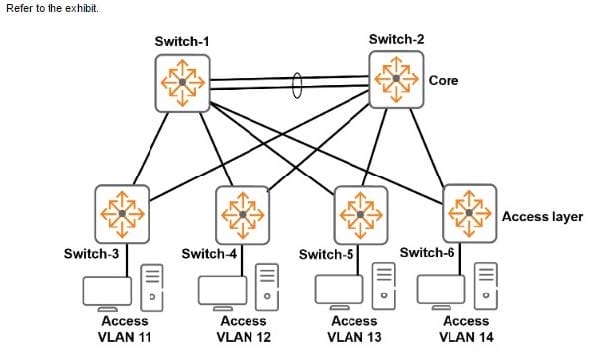
This exhibit shows the topology for a company campus LAN. Each access layer switch will be the default router for the devices connected to it. The company needs to permit the following:
1.
Communications between devices in an subnets
2.
Support for efficient traffic paths during normal operation and in situations in which a link fails
3.
Fast failover if a link fails
Which feature should the network administrator configure on the ArubaOS switches to support these requirements?
A. MSTP
B. RIP
C. Static Routes
D. OSPF
A port on an ArubaOS switch has its default spanning tree settings. When is the port defined as a spanning tree edge port?
A. when the switch and the connected switch run MSTP but have different region settings
B. when the switch runs MSTP but the connected switch runs RSTP
C. when the port fails to receive BPDUs on the port within a set period of time
D. when the port is part of a VLAN that is dedicated to that port alone
