FINANCIAL-ACCOUNTING-AND-REPORTING Online Practice Questions and Answers
Which of the following is true regarding the comparison of managerial to financial accounting?
A. Managerial accounting is generally more precise.
B. Managerial accounting has a past focus and financial accounting has a future focus.
C. The emphasis on managerial accounting is relevance and the emphasis on financial accounting is timeliness.
D. Managerial accounting need not follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) while financial accounting must follow them.
On December 2, 20X1, Flint Corp.'s board of directors voted to discontinue operations of its frozen food division and to sell the division's assets on the open market as soon as possible. The division reported net operating losses of $20,000 in December and $30,000 in January. On February 26, 20X2, sale of the division's assets resulted in a gain of $90,000. Assuming that the frozen foods division qualifies as a component of the business and ignoring income taxes, what amount of gain/loss from discontinued operations should Flint recognize in its income statement for 20X2?
A. $0
B. $40,000
C. $60,000
D. $90,000
Lore Co. changed from the cash basis of accounting to the accrual basis of accounting during 1994. The cumulative effect of this change should be reported in Lore's 1994 financial statements as a:
A. Prior period adjustment resulting from the correction of an error.
B. Prior period adjustment resulting from the change in accounting principle.
C. Component of income before extraordinary item.
D. Component of income after extraordinary item.
Envoy Co. manufactures and sells household products. Envoy experienced losses associated with its small appliance group. Operations and cash flows for this group can be clearly distinguished from the rest of Envoy's operations. Envoy plans to sell the small appliance group with its operations. What is the earliest point at which Envoy should report the small appliance group as a discontinued operation?
A. When Envoy classifies it as held for sale.
B. When Envoy receives an offer for the segment.
C. When Envoy first sells any of the assets of the segment.
D. When Envoy sells the majority of the assets of the segment.
Which of the following should be disclosed in a summary of significant accounting policies?
A. Basis of profit recognition on long-term construction contracts.
B. Future minimum lease payments in the aggregate and for each of the five succeeding fiscal years.
C. Depreciation expense.
D. Composition of sales by segment.
During the first quarter of 1993, Tech Co. had income before taxes of $200,000, and its effective income tax rate was 15%. Tech's 1992 effective annual income tax rate was 30%, but Tech expects its 1993 effective annual income tax rate to be 25%. In its first quarter interim income statement, what amount of income tax expense should Tech report?
A. $0
B. $30,000
C. $50,000
D. $60,000
Taft Corp. discloses supplemental industry segment information. The following information is available for 1992: Additional 1992 expenses, not included above, are as follows:
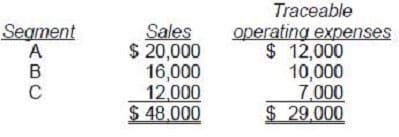
Indirect operating expenses $7,200 General corporate expenses 4,800
Segment C's 1992 operating profit was:
A. $5,000
B. $3,200
C. $2,600
D. $2,000
In financial reporting of segment data, which of the following items is always used in determining a segment's operating income?
A. Income tax expense.
B. Sales to other segments.
C. General corporate expense.
D. Gain or loss on discontinued operations.
Which of the following types of entities are required to report on business segments?
A. Nonpublic business enterprises.
B. Publicly-traded enterprises.
C. Not-for-profit enterprises.
D. Joint ventures.
According to the FASB conceptual framework, an entity's revenue may result from:
A. A decrease in an asset from primary operations.
B. An increase in an asset from incidental transactions.
C. An increase in a liability from incidental transactions.
D. A decrease in a liability from primary operations.
On March 15, 1992, Krol Co. paid property taxes of $90,000 on its office building for the calendar year 1992. On April 1, 1992, Krol paid $150,000 for unanticipated repairs to its office equipment. The repairs will benefit operations for the remainder of 1992. What is the total amount of these expenses that Krol should include in its quarterly income statement for the three months ended June 30, 1992?
A. $172,500
B. $97,500
C. $72,500
D. $37,500
On January 2, 1993, Quo, Inc. hired Reed to be its controller. During the year, Reed, working closely with Quo's president and outside accountants, made changes in accounting policies, corrected several errors dating from 1992 and before, and instituted new accounting policies. Quo's 1993 financial statements will be presented in comparative form with its 1992 financial statements. This question represents one of Quo's transactions. List A represents possible clarifications of these transactions as: a change in accounting principle, a change in accounting estimate, a correction of an error in previously presented financial statements, or neither an accounting change nor an accounting error.
Item to Be Answered Quo sells extended service contracts on its products. Because related services are performed over several years, in 1993 Quo changed from the cash method to the accrual method of recognizing income from these service contracts.
List A (Select one)
A. Change in accounting principal.
B. Change in accounting estimate.
C. Correction of an error in previously presented financial statements.
D. Neither an accounting change nor an accounting error.
On January 2, 1993, Quo, Inc. hired Reed to be its controller. During the year, Reed, working closely with
Quo's president and outside accountants, made changes in accounting policies, corrected several errors
dating from 1992 and before, and instituted new accounting policies.
Quo's 1993 financial statements will be presented in comparative form with its 1992 financial statements.
This question represents one of Quo's transactions. List B represents the general accounting treatment
required for these transactions. These treatments are:
•
Cumulative effect approach - Include the cumulative effect of the adjustment resulting from the accounting change or error correction in the 1993 financial statements, and do not restate the 1992 financial statements.
•
Retroactive or retrospective restatement approach - Restate the 1992 financial statements and adjust 1992 beginning retained earnings if the error or change affects a period prior to 1992.
•
Prospective approach - Report 1993 and future financial statements on the new basis but do not restate 1992 financial statements.
Item to Be Answered Quo sells extended service contracts on its products. Because related services are performed over several years, in 1993 Quo changed from the cash method to the accrual method of recognizing income from these service contracts.
List B (Select one)
A. Cumulative effect approach.
B. Retroactive or retrospective restatement approach.
C. Prospective approach.
On January 2, 1993, Quo, Inc. hired Reed to be its controller. During the year, Reed, working closely with
Quo's president and outside accountants, made changes in accounting policies, corrected several errors
dating from 1992 and before, and instituted new accounting policies.
Quo's 1993 financial statements will be presented in comparative form with its 1992 financial statements.
This question represents one of Quo's transactions. List A represents possible clarifications of these
transactions as: a change in accounting principle, a change in accounting estimate, a correction of an error
in previously presented financial statements, or neither an accounting change nor an accounting error.
During 1993, Quo increased its investment in Worth, Inc. from a 10% interest, purchased in 1992, to 30%,
and acquired a seat on Worth's board of directors. As a result of its increased investment, Quo changed its method of accounting for investment in Worth, Inc. from the cost method to the equity method.
List A
A. Change in accounting principle.
B. Change in accounting estimate.
C. Correction of an error in previously presented financial statements.
D. Neither an accounting change nor an accounting error.
On January 2, 1993, Quo, Inc. hired Reed to be its controller. During the year, Reed, working closely with
Quo's president and outside accountants, made changes in accounting policies, corrected several errors
dating from 1992 and before, and instituted new accounting policies.
Quo's 1993 financial statements will be presented in comparative form with its 1992 financial statements.
This question represents one of Quo's transactions. List B represents the general accounting treatment
required for these transactions. These treatments are:
•
Cumulative effect approach - Include the cumulative effect of the adjustment resulting from the accounting change or error correction in the 1993 financial statements, and do not restate the 1992 financial statements.
•
Retroactive or retrospective restatement approach - Restate the 1992 financial statements and adjust 1992 beginning retained earnings if the error or change affects a period prior to 1992.
•
Prospective approach - Report 1993 and future financial statements on the new basis but do not restate 1992 financial statements.
During 1993, Quo increased its investment in Worth, Inc. from a 10% interest, purchased in 1992, to 30%, and acquired a seat on Worth's board of directors. As a result of its increased investment, Quo changed its method of accounting for investment in Worth, Inc. from the cost method to the equity method.
List B
A. Cumulative effect approach.
B. Retroactive or retrospective restatement approach.
C. Prospective approach.


