CPHQ Online Practice Questions and Answers
In the 1970s, Deming developed his 14 points for western Management in response to requests from U.S. managers for the secret to the radical improvement that Japanese companies were achieving in a number of industries. As part of his "system of profound knowledge," Deming promoted that "around 15% of poor quality was because of workers, and the rest of 85% was due to bad management, improper systems and processes." The "system" is based on parts.
Which of the following is/are NOT out of those parts?
A. Appreciation for a system
B. Knowledge about variation
C. Theory of knowledge
D. Sociology
The following diagram shows: A. Baldrige criteria for improvement
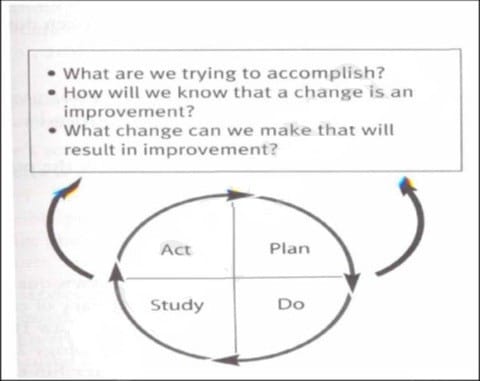
B. API Improvement model
C. Quality improvement
D. None of these
By using a set of statistical tools to understand the fluctuation of a process, management can predict the expected outcome of that process. If the outcome is not satisfactory, management can use associated tools to further understand the elements influencing that process.
Six sigma includes process steps which are commonly known as ____________.
A. DAMIC
B. PDCA
C. DAMIE
D. PDSA
The primary purpose of a management information system is to:
A. Provide data for quality assessment.
B. Computerize operations for greater effectiveness.
C. Guarantee better coordination of organizational change.
D. Provide information that facilitates management decisions.
The concept of cost-effectiveness in Healthcare delivery means:
A. A proportionately justified improvement in health status of patient is obtained comparing to the cost incurred.
B. Little improvement in Health status of patient is obtained at a very high cost
C. Little improvement in Health status of patient is obtained at a very low cost
D. Great improvement in Health status of patient is obtained at a very low cost
_______________ is based on a simple principle-statistical probability. In other words, within a known population of size n, there will be a fixed probability of selecting any single element.
A. Probability sampling
B. Random sampling
C. Systematic sampling
D. Non-probability sampling
Examples of administrative data sources are all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Hospital or physician office billing systems
B. Health plan claim databases
C. Health information management or medical record system
D. Nursing management system
Health care provider accountability Decision making public reporting Organizational evaluation National performance improvement goals and activities
These are the performance measures identified by health organizations in order to meet:
A. Internal needs specifically
B. External needs specifically
C. Organizational vision
D. Organizational objective
Feedback from patients and their families will provide rich information for quality improvement work. For these efforts to be successful, you should consider some questions.
Which of the following is NOT out of those questions?
A. What is your aim for improvement?
B. Who will review the data?
C. What was your last year budget?
D. How frequently do you need to measure your performance to achieve your name?
A patient was in the operating room when a piece of a surgical instrument broke off and was left in the patient's body. The patient was readmitted for removal of the foreign object.
Which of the following would most likely apply in this situation?
A. Res ipsa loquitur
B. Contributory negligence
C. Contractual liability
D. Tort liability
Which of the following types of budgets itemizes the major equipment to be purchased in the next year?
A. Capital
B. Variable
C. Operating
D. Zero-based
Familiarity with terms describing the psychometric properties of survey instruments and methods for data collection can help an organization choose a survey that will provide it with credible information for quality improvement. There are two different and complementary approaches to assessing the reliability and validity of a questionnaire.
Which of the following are out of those approaches?
A. Cognitive testing
B. Technical excellence testing
C. Psychometric testing
D. Both A and C
Weighting of scores is frequently recommended if members of a (patients) population have unequal probabilities of being selected for the sample. If necessary, weights are assigned to the different observations to provide a representation picture of the total population.
Weighting should be considered when
A. An equal distribution of patients exists by discharge service, nursing unit, or clinic
B. An unequal distribution of patients exists by discharge service, nursing unit, or clinic
C. An unequal distribution of patients exists by laboratories
D. An equal distribution of patients exists by ICUs
Case-mix adjustment accounts for the different types of patients in institutions. Adjustment should be
considered when hospital survey results are being released to the public.
The characteristics commonly associated with the patient reports on quality of care are all of the following
EXCEPT:
(Choose two.)
A. Patient age (i.e., older patients tend to report fewer problems with care)
B. Discharge service (e.g., childbirth patients evaluate their experiences more favorably than do medical or surgical patients; medical patients report the most problems with care)
C. Patient satisfaction
D. Number of visits to the hospitals
Once listing posts system is in place, root-cause analyses can be performed to identify particular problems, such as a staff member or medical group that contributes to problems, or problems that are systemic to the delivery of care, such as an antiquated manual appointment system.
Listing post strategies include: (Choose two.)
A. Surveys
B. Focus group
C. Patient and family advisory services
D. Suggestion boxes
