ASCP-MLT Online Practice Questions and Answers
Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions are most commonly due to ABO-incompatible blood being transfused to a recipient with naturally occurring ABO alloantibodies (anti-A, anti-B, anti A,B). Acute intravascular hemolysis as the result of a blood transfusion is most often associated with which of the following causes?
A. Transfusion of ABO incompatible red cells
B. Allergies
C. Passively transfused antibodies to HLA antigens
D. Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease
The document designed to protect phlebotomists from contacting hepatitis is the:
A. Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan
B. Chemical Hygiene Plan
C. Material Safety Data Sheets
D. procedure manual
The red blood cell distribution width (RDW) increases as the severity of alpha thalassemia increases because of changing MCV as the bone marrow produces smaller cells. In addition, if Hemoglobin H bodies are present, they result in the formation of schiztocytes (RBC fragments) that can have an effect on the MCV and RDW.
The Red cell Distribution Width (RDW) in alpha thalassemia is
A. within normal limits
B. usually increased
C. usually decreased
D. dependent upon severity
The microscopic features shown here represent Scopulariopsis species. In most instances, particularly if a patient does not have underlying immunologic or hematologic disease, Scopulariopsis species should be considered a contaminant
when recovered from a sputum specimen. However, if there is clinical or X-ray evidence of mycotic pulmonary infection, additional daily induced sputum specimens should be obtained.
If Scopulariopsis species or any other hyaline mold is recovered from two or more successive specimens, its potential as a pathogenic agent should be considered. Scopulariopsis species have been reported as the agents of pulmonary
fungus ball infections in patients with preexistent cavities and as a cause of pneumonia in patients with leukemia.
Invasive pulmonary disease by this agent has not been reported.
The fungus illustrated in this photomicrograph was recovered from an induced sputum specimen from a 74 year old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This isolate is most likely:
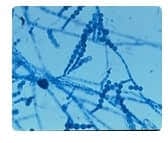
A. The cause of chronic bronchitis
B. The cause of invasive pulmonary disease
C. The cause of allergic bronchopulmonary disease
D. A contaminant
The Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act requires employers to:
A. test MLTs annually for hepatitis B and HIV
B. involve MLTs in the selection of safety devices
C. provide MLTs with plastic capillary tubes
D. allow MLTs to work flexible schedules
To make a 1 : 10 dilution, 270 μL of diluent should be added to 30 μL of sample, .
A spinal fluid that is slightly hazy is briefly examined microscopically. The technologist performing the count decides to make a 1:10 dilution using 30 μL of sample. What volume of diluent should be used?
A. 70 μL
B. 270 μL
C. 300 μL
P. vivax characteristically displays Schuffner's dots and often enlarged RBCs along with brownish granules. P. vivax can also have 12-24 merozoies in each cell, actually filling the entire RBC. This parasite also has very irreglar shapes often referred to as "Ameboid".
P. falciparum and P. malariae do not display Shuffner's dots, therefore could not be the correct choice.
P. ovale does display Shuffner's dots in all stages, but characteristically has about 8-12 merozoites in rosettes or irregular clusters inside the RBC. Also, P. ovale characteristically shows enlarged, ovoid RBCs with fimbriated edges. Identify the parasite of a patient with suspected malaria who demonstrates the following findings on a blood smear:
-Enlarged RBCs, some with fine brownish granules
-> 15 parasites in some cells
-Ameboid structures
-
Schuffner's dots
A.
Plasmodium falciparum
B.
Plasmodium ovale
C.
Plasmodium vivax
D.
Plasmodium malariae
Blood Bank
What other component(s) can be shipped together with Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)?
A. frozen RBC's and cryoprecipitate
B. platelets
C. packed RBC's and granulocytes
D. whole blood
E. none
Creatinine clearance tests are utilized to estimate the glomerular function of the kidney. The creatitine clearance calculation is defined as the volume of plasma that is cleared of creatinine by the kidney per unit of time and uses the following
formula:
creatinine clearance = Urine creatinine conc x Volume / Plamsa creatinine conc
Creatinine clearance measurements have a recommended specimen requirement = 24- hour urine collection.
Which of the following tests would be useful in the assessment of glomerular filtration:
A. 24 hour urine protein
B. Creatinine clearance
C. PSP test
D. Urea clearance
Nucleated RBCs may be seen in the peripheral blood in cases of beta thalassemia major. Nucleated RBCs are usually not found in peripheral blood in cases of beta thalassemia minor and beta thalassemia intermedia, and would not be a finding in beta thalassemia minima.
Nucleated RBCs are most likely to be seen in the peripheral blood of which of these beta thalassemias?
A. Beta thalassemia minima
B. Beta thalassemia minor
C. Beta thalassemia intermedia
D. Beta thalassemia major
Although cysteine-blood agar was traditionally used, F. tularensis will also grow on commercially available Thayer-Martin and chocolate agar which have been enriched with supplemental nutrients. Which of the following media would you use to isolate Francisella tularensis:
A. Sheep-blood agar
B. Lowenstein-Jensen media
C. Bordet-Gengou media
D. Cysteine-blood agar
Specimens collected from patients in contact isolation should be:
A. Collected in duplicate.
B. double-bagged.
C. delivered to microbiology.
D. collected wearing sterile gloves.
In which disorder do neonates demonstrate the presence of Bart's hemoglobin that changes to beta chain tetramers in adults?
A. Alpha thalassemia major
B. Alpha thalassemia minor
C. Hemoglobin H disease
D. Hydrops fetalis
If a drug is given at intervals that are the same as its half-life, it will take about 5 half-lives to reach steady state.
If a drug is given at intervals that are the same as its half-life, approximately how long will it take the drug to reach steady state?
A. It will be at steady state from the first dose.
B. It will take about two half-lives to reach steady state.
C. It will take about 5 half-lives to reach steady state.
D. It will never reach a steady state.
Report the isolate as coagulase negative Staphylococcus is the correct answer because this is an isolate from a urine specimen with a coagulase negative Staphylococcus susceptible to novobiocin. Staphylococcus saprophyticus is resistant to novobiocin. Further testing is required to speciate coagulase negative Staphylococci but only if the specimen is from a sterile body site, not urine. Gram positive cocci isolated from a catheterized urine culture on a 76-year-old male gave the following reactions: Blood agar- creamy, white, opaque colonies Catalase- positive Slide coagulase- negative Tube coagulase- negative Novobiocin- susceptible The next action the MLS should take is:
A. Report the isolate as coagulase negative staphylococcus
B. Report the isolate as Staphylococcus epidermidis
C. Report the isolate as Staphylococcus saprophyticus
D. Perform further testing to speciate the organism
