ACLS Online Practice Questions and Answers
In therapeutic doses, which drug depresses the pumping function of the heart muscle?
A. atropine
B. epinephrine
C. propanolol
D. isoproterenol
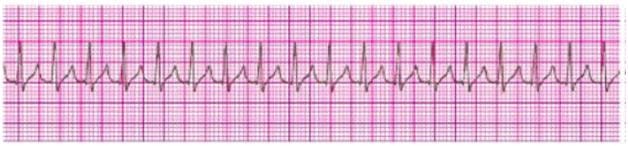
A 35-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of palpitations. She has no chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or lightheadedness. Which of the following is indicated first?
A. Give adenosine 3 mg IV bolus
B. Give adenosine 12 mg IV slow push (over 1 to 2 minutes)
C. Perform vagal maneuvers
D. Give metoprolol 5 mg IV and repeat if necessary
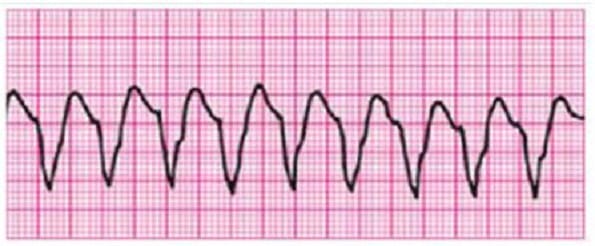
You are monitoring a patient. Chest discomfort has been relieved with sublingual nitrates and morphine sulfate 4 mg IV. He suddenly has the above persistent rhythm. You ask about symptoms and he reports mild palpitations, but otherwise he is clinically stable with unchanged vital signs. Your next action is:
A. Give sedation and perform synchronized cardioversion
B. Administer amiodarone 150 mg over 10 minutes; seek expert consultation
C. Give immediate synchronized shock
D. Give immediate unsynchronized shock
E. Administer magnesium sulfate 1 to 2 g IV diluted in 10 mL D5W given over 5 to 20 minutes
I A 57-year-old woman has palpitations, chest discomfort and tachycardia. The monitor shows a regular wide-complex QRS at a rate of 180 per minute. She becomes diaphoretic and blood pressure is 80/60 mmHg. The next action is to:
A. Establish IV and give sedation for electrical cardioversion
B. Give amiodarone 300 mg IV push
C. Obtain 12 lead electrocardiogram
D. Perform immediate electrical cardioversion
T/F: Epinephrine increases cerebral and myocardial blood flow during CPR.
A. False
B. True
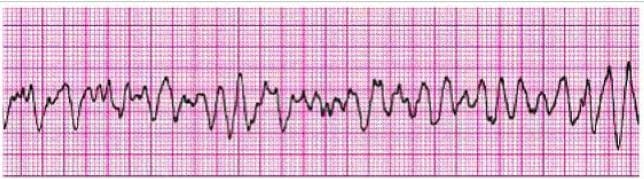
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
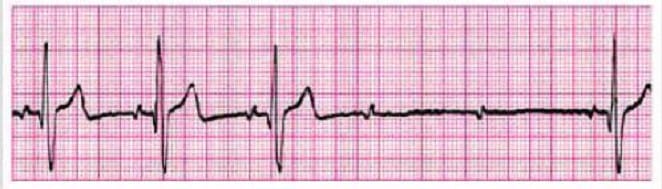
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
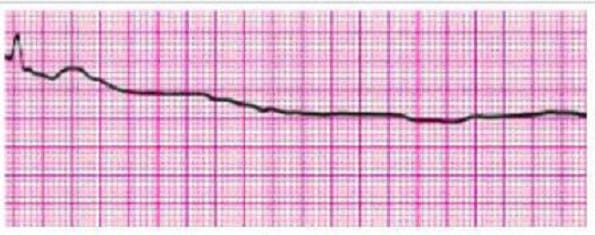
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
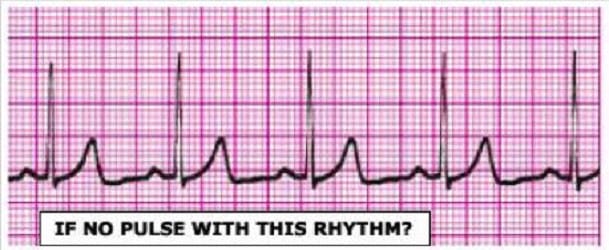
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
FILL BLANK
After the child is removed from the water, what is the top priority in near drowning cases?
A. Artificial ventilation
FILL BLANK
Following successful resuscitation from ventricular fibrillation, patients should be treated with:
A. oxygen, lidocaine
SIMULATION
Describe the proper technique for assessing circulation in infants and children.
A. When assessing the circulatory status of a child, the following need to be examined: the brachial or femoral pulse, peripheral pulses, capillary refill, skin color, and temperature. Blood pressure should be assessed in children over the age of 3.
FILL BLANK
What is the legal term for unlawfully touching a patient without his or her consent?
A. Battery
SIMULATION Define negligence.
A. Negligence is the deviation from the accepted standard of care resulting in further injury to the patient.
