CSQA Online Practice Questions and Answers
Which of the following defines special cause of variation?
A. Variation between the upper and lower control limits
B. Variation not present in the process
C. Conditions that regularly contribute to variability
D. Contributes a small portion to control variation of process outputs
E. Regular contributors to variability
In transaction processing, the accuracy and completeness of database storage, data security and privacy, error handling, backup, recovery, and retention is governed by:
A. Transaction Origination Controls
B. Transaction Processing Controls
C. Transaction Output Controls
D. Database Storage and Retrieval Controls
Correlation between process maturity and an organization's willingness to embrace change can be described as:
A. Accelerates at the lower levels and lags during the higher levels of maturity
B. Lags slightly at the lower levels and accelerates during the higher levels of maturity
C. Accelerates at same rate at all levels
D. None of the above
Who is responsible to ensure that the organization has sufficiently trained personnel to protect its IT resources?
A. CIO / IT Director
B. Management
C. Delivery Manager
D. Director
Experience has shown statistically that as program modules become more complex:
A. The time to develop the module decreases
B. The amount of effort to test the validity increases geometrically
C. The number of defects has an inverse relationship
D. The tester needs to segment the program
E. The need for a help desk increases
The focus of post-implementation reviews or post mortems is to:
A. Correct the defects
B. Improve the process
C. Plan future projects
D. Fix the blame for bad quality
E. None of the above
These five components (environment, risk assessment, control activities, information communication, and monitoring) are associated with which of the following control models:
A. COSO Internal Control Framework Model
B. ISO Model
C. Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award Model
D. Enterprise Risk and Management Model
E. CobiT Model
One of the tools used to analyze process improvement results is:
A. Developing measurement capability: Pie Charts
B. Analyzing results: Control Charts
C. Identifying advanced statistical techniques: QFD
D. Identifying data collection tools: Force Field Analysis
As the type of product changes on the process maturity continuum, the work processes also change.
A. True
B. False
Checking if the web page on a internet banking site comes up within 2 seconds is an example of:
A. Functional Testing
B. Structural Testing
C. Stress Testing
D. Performance Testing
E. White-Box Testing
If an organization was to categorize risks as critical, major, or minor what aspect of Risk Management would that be called?
A. Risk Prioritization
B. Risk Response Planning
C. Risk Resolution
D. Risk Analysis
E. Risk Monitoring
Critical Success Factors (CSF) are those criteria or factors that:
A. Are critical to be defined
B. Must be present in acquired software
C. Are very desirable in the acquired software
D. Will be defined during acceptance testing
E. Are limited to functional requirements
Conducting an inspection of source code is:
A. Quality Control
B. Compilation
C. Quality Assurance
D. None of the above
Audits can be performed by the individuals involved in conducting the work.
A. True
B. False
-- Exhibit
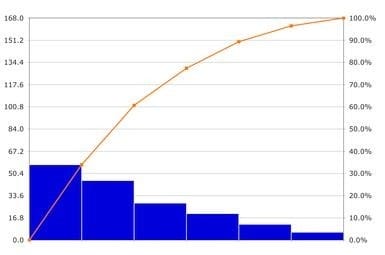
-- Exhibit -The diagram is called a:
A. Run Chart
B. Pie Chart
C. Bar Chart
D. Pareto Chart
E. Control Chart
