300-510 Online Practice Questions and Answers
What is used by SR-TE to steer traffic through the network?
A. shortest path calculated by IGP
B. dynamic rules
C. path policy
D. explicit maps
Refer to the exhibit.

Router 1 is connected to router 2 on interface TenGigE0/1.
Which interface provides the alternate path to 172.16.200.9/32 when the link between router 1 and router 2 goes down?
A. TenGigE0/1 interface provides the alternate path
B. A backup path must be statically installed
C. TenGigE0/2 interface provides the alternate path
D. A primary path must be manually installed
You have configured routing policies on a Cisco IOS XR device with routing policy language. Which two statements about the routing policies are true? (Choose two.)
A. The routing policies affect BGP-related routes only.
B. If you make edits to an existing routing policy without pasting the full policy into the CLI, the previous policy is overwritten.
C. You can change an existing routing policy by editing individual statements.
D. The routing policies are implemented in a sequential manner.
E. The routing policies are implemented using route maps.
Refer to the exhibit.
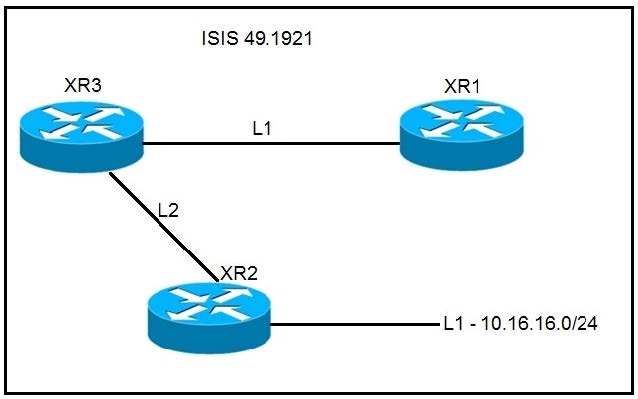
A network operator must inject a Level 1 route from XR2 (10.16.16.0/24) into the ISIS topology.
Which configuration allows the injection in a way that XR3 and XR1 have a valid and working route for 10.16.16.0/24?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
In a PIM-SM environment, which mechanism determines the traffic that a receiver receives?
A. The receiver explicitly requests its desired traffic from the RP on the shared tree.
B. The receiver explicitly requests traffic from a single source, which responds by forwarding all traffic.
C. The RP on the shared tree floods traffic out of all PIM configured interfaces.
D. The receiver explicitly requests traffic from each desired source, which responds by sending all traffic.
Refer to the exhibit.
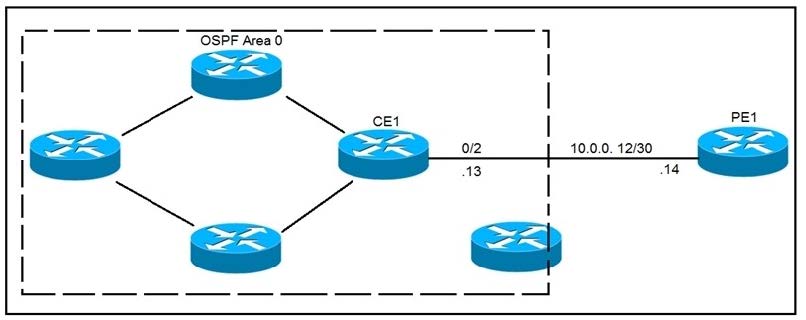
CE1 is the gateway router into the provider network via PE1. A network operator must inject a default route into OSPF area 0. All devices inside area 0 must be able to reach PE1. Which configuration achieves this goal?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
An engineer is working to implement segment routing protocol on the customer's core network. Which step should the engineer take before the segment routing is enabled and is running with BGP?
A. Segment routing must be configured with ISIS.
B. Segment routing must be configured with EIGRP.
C. Explicit-null must be configured for all neighbors.
D. MPLS must be configured.
What are two differences between OSPF and IS-IS? (Choose two.)
A. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol, and IS-IS is a distance-vector routing protocol.
B. OSPF uses a router ID to identify a router, and IS-IS uses a system ID.
C. OSPF elects a DR and a BDR, and IS-IS elects a DIS.
D. Unlike OSPF. IS-IS supports virtual links.
E. Unlike IS-IS routers, an OSPF router belongs to only one area in addition to the backbone area.
Refer to the exhibit.
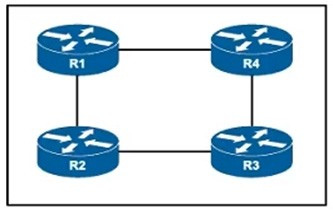
All routers on this network have been configured with PIM-SM, and R1 is the rendezvous point. However, when asymmetric routing is implemented to modify link usage, the network begins to drop certain multicast traffic. Which action corrects the problem?
A. Place the routes affected by asymmetric routing in a VRF
B. Remove the asymmetric routing and use spanning tree to manage link usage
C. Add a static mroute for routes that are failing
D. Configure the routers to use PIM-DM instead of PIM-SM
Refer to the exhibit.
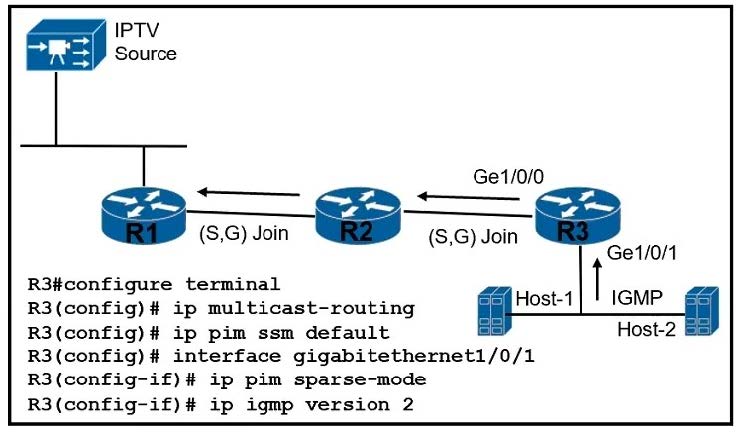
A customer reports that Host-1 is failing to receive streaming traffic from the IPTV source. The engineer has confirmed that hosts on router R2 are receiving traffic normally and that Host-1 is correctly sending subscription messages to join the IPTV stream. Which action must the engineer take to correct the problem?
A. Remove IP PIM SSM and IGMP from interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on R3 and configure under global configuration
B. Configure IGMP version 3 under interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on R3
C. Configure IP PIM SSM and IGMP version 2 under interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on R3
D. Remove IP PIM SSM from the global configuration on R3 and configure it under the GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 interface
Refer to the exhibit.
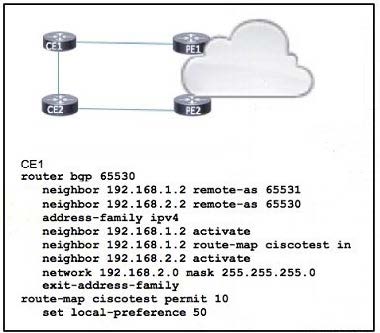
Routers CE1 and CE2 are in AS 65530. which is multihomed for Internet access.
An engineer expects inbound traffic to AS 65530 to arrive from PE1. but it is coming from PE2 instead PE1 and PE2 routers are connected with CE routers through the same bandwidth
Which action must be taken to correct the problem?
A. On router CE2, configure inbound routes from PE2 to CE2 with a local-preference value of 50 or greater.
B. Configure router CEI to prepend the AS path to routes it receives from PE 1.
C. Set the local-preference value on router CEI to 100 or greater
D. On router PEI , change the origin for routes that are redistributed from CEI to CE2.
Refer to the exhibit.
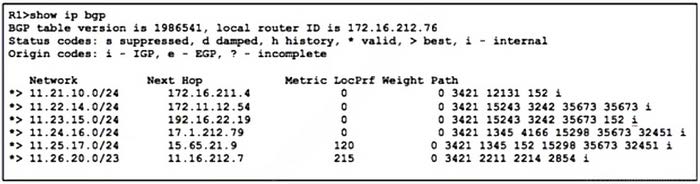
Company A established BGP sessions with several ISPs. A network engineer at the company must filter out all traffic except for routes that transit AS 152.
The engineer configured the filtering policy "permit _152S_(_[0.9])" on R1, but after applying the configuration, the engineer notices that other routes are still visible.
Which action resolves the issue?
A. Add a second filtering policy in the format ip access-list 1 permit ^152_([0-9]+).
B. Add a second filtering policy in the format ip prefix-list 1 permit ^152^.
C. Change the filtering policy to ip explicit-path 1 permit $152^.
D. Change the filtering policy to ip as-path access-list 1 permit _152_.
Refer to the exhibit.

After configuring IS-IS on routers R1 and R2, an engineer notices that only the loopback interface at 2000:1::1 /96 is known to router R2. Which change must be made so that only Loopback2 is advertised from R1 to R2?
A. Configure the router isis area1 command under the Loopback0 interface on R1.
B. Remove the advertise passive-only command under the IS-IS address family ipv6 configuration
C. Remove the ipv6 router isis area1 command under the Loopback2 interface on R1.
D. Remove the passive-interface Loopback0 command under the router isis area1 configuration.
While configuring Cisco NSF awareness, a network engineer enters the bgp graceful-restart command after the BGP session is established in a router that runs IOS XE Software. Graceful restart capabilities are not exchanged. Which two actions should be taken? (Choose two.)
A. Reload the router
B. Verify that BGP route dampening is configured
C. Reduce BGP convergence time
D. Issue the clear ip bgp * command
E. Issue the show ip bgp neighbors command.
What is the difference between a source tree and a shared tree in a multicast environment?
A. To route traffic from source to receiver a source tree uses a link-state routing protocol and a shared tree uses a distance-vector routing protocol.
B. A source tree has its root at the source, and a shared tree has its root at a designated rendezvous point.
C. To stream multicast from source to receiver, a source tree uses PIM-SM and a shared tree uses PIM-DM.
D. Source trees are the default type for bidirectional PIM, and PIM-DM uses shared trees by default.
