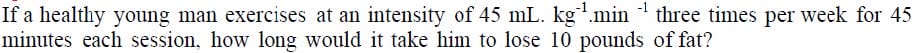030-333 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Initial training sessions for a person with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease most likely would NOT include.
A. Continuous cycling activity at 70% ofVo
B. Use of dyspnea scales, RPE scales, and pursed-lip breathing instruction.
C. Intermittent bouts of activity on a variety of modalities (exercise followed by short rest).
D. Encouraging the client to achieve an intensity either at or above the anaerobic threshold.
In an effort to improve flexibility, the ACSM recommends:
A. Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation.
B. Ballistic stretching.
C. The plough and hurdler's stretches.
D. Static stretches held for 10 to 30 seconds per repetition.
Which of the following statements true regarding exercise leadership is FALSE?
A. The exercise leader should be fit enough to exercise with any of his or her participants.
B. Most people are not bored by exercise and can easily find time to participate in an exercise program.
C. The exercise leader should adjust the exercise intensity based on individual differences in fitness.
D. Periodic fitness assessment may provide evidence of improvement in fitness for some participants.
Which of the following medications have been shown to be most effective in preventing or reversing exercise-induced asthma?
A. f3 -Agonists.
B. f3 -Blockers.
C. Diuretics.
D. Aspirin.
All of the following factors are important to consider when determining exercise intensity EXCEPT:
A. An individual's level of fitness.
B. The risk of cardiovascular or orthopedic injury.
C. Any previous history participating in organized sports.
D. Individual preference and exercise objectives.
When counseling a patient with metabolic syndrome, your emphasis should be on addressing underlying causes of the syndrome, such as:
A. Obesity and physical inactivity.
B. Excessive carbohydrate intake.
C. Elevated LDL-C concentration.
D. Lack of muscular strength.
Which of the following is not a feature of the metabolic syndrome?
A. Dyslipidemia (low HDL-C, elevated triglycerides).
B. Osteoporosis.
C. Insulin resistance.
D. Elevated blood pressure.
Which energy source represents the largest potential energy store in the body?
A. Fat.
B. Blood glucose.
C. Muscle glycogen.
D. Protein.
Program description, resource availability, and client interest are examples of:
A. A business plan.
B. A survey.
C. Management factors.
D. Budget categories.
Why are records valuable to a fitness program?
A. They help in evaluation of a program.
B. They offer music not found on tapes or CDs.
C. They help to provide facts in any legal issues.
D. They help the front desk to monitor paid and unpaid clients.
Examples of program records include:
A. Client progress and outcomes.
B. Member needs.
C. Performance of clients on selected exercises.
D. Member suggestions and any actions taken regarding them.
A 110-pound female pedals a Monark cycle ergometer at 50 rpm against a resistance of 2.5 kiloponds. Calculate her absolute Yo2.

A. B. C. D.
In the ECG strip shown below, which arrhythmia is indicated?
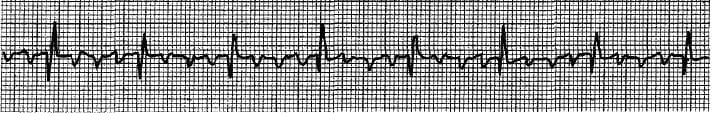
A. Atrial flutter.
B. Atrial fibrillation.
C. Premature atrial contractions.
D. Atrial tachycardia.
In response to various stimuli, movements of ions occur, causing the rapid loss of the internal negative potential. This process is known as:
A. Polarization.
B. Repolarization.
C. Automaticity.
D. Depolarization.